Property Rights Regimes Are Classified Under What Basis
These resources can be both tangible or intangible and can be owned by individuals businesses and. Public ownership of the means of production was a key feature that distinguished Soviet law from the law of most other dictatorial police states.
 The Industry Leading Intellectual Property Consultancy Infographic Intellectual Property Law Creativity And Innovation
The Industry Leading Intellectual Property Consultancy Infographic Intellectual Property Law Creativity And Innovation
The intervention refers to an existing property regime or introduction or change in the particular property rights regime under study.
Property rights regimes are classified under what basis. Complete Separation of Property 2. Business freedom has an affect on property rights. The rights of physical access withdrawal management exclusion and alienation.
2 question Property rights regimes are classified under what basis. Property rights matters because of the presence of subsequent noncontractible actions andor imperfect negotiations but in which their optimal allocation amounts to more than a case 4Note however that when utilities are not quasilinear there are wealth effects final outcomes will typically depend on the property rights specified in stage 1. As Hardin recognized where property rights are well-defined and secure the tragedy of the commons is less likely for each owner has ample incentive to act as a steward caring for the underlying.
Common property regimes arise in situations where appropriators acting independently in relationship to a common-pool resource generating scarce resource units would obtain a lower total net benefit than what is achieved if they coordinate their strategies in some way maintaining the resource system as common property instead of dividing it up into bits of private property. Intellectual property rights are the rights given to persons over the creations of their minds. Property rights are basic human rights grounded in current Human Rights law as found in article 17 of The Universal Declaration of Human Rights and theoretical constructs in economics for determining how a resource or economic good is used and owned.
Limiting one type of freedom limits all freedoms. In the course of it thinking shifted farther and farther away from any conception of the property basis of rights. Additionally a combination of two or more of these regimes mixed regimes and open access situations where access and withdrawal rights were open to anyone are also considered in the review.
We find different forms of property. The ability for individuals to own private property that is acknowledged by its respective country. 3 Underlying the distinction is the idea that rights are nested ie that the first-order rights of access and withdrawal depend on the exercise of the second-order rights of management exclusion and alienation Ostrom 1994.
A right to property is recognised in Article 17 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights but it is not recognised in the International Covenant. The property rights can be held under either of four different regimes. Within a private property rights regime individuals need the ability to exclude others from the uses and benefits of their property.
Property may be broadly classified into two types private property and common public property. In fact they are one of the main foundations of a free society. Private property rights then are a social institution which tends to bring about peace and harmony in a society of free people.
Key Variables Property Rights. It will be my contention here that this almost totally obscured the means for establishing any rights. Property rights are the social institutions that define or delimit the range of privileges granted to individuals of specific resources such as parcels of land or water.
There can be no personal or political freedom without freedom in the use of ones property. The law distinguished between socialist property and individually owned private property. Socialist property included two subcategoriesstate property and collective or cooperative propertyboth of which were subject to virtually identical regimes of central economic planning.
Schlager and Ostroms 1992 conceptual schema distinguishes five types of property rights. The scale is from 10-90 which 10. It is necessary then to explore the property basis of rights.
Property rights define the theoretical and legal ownership of resources and how they can be used. Open access public common and private property regimes Swanson and Barbier. A good place to begin is with a definition of right.
The nature of property rights and type of property vary from society to society and within a particular society over time because property rights are socially terminated. The rights of authors of literary and artistic works such as books and other writings musical compositions paintings sculpture computer programs and films are protected by copyright for a minimum period of 50 years after the death of the author. Private ownership of these resources may involve a variety of property rights including the right to exclude nonowners from access the right to appropriate the stream of economic.
A general recognition of a right to private property is found more rarely and is typically heavily constrained insofar as property is owned by legal persons and where it is used for production rather than consumption. All privately owned resources are rivalrous meaning only a. Property regime is understood as a system of rules that govern access to and control over resources encompassing state private or community regimes.
The right to property or right to own property is often classified as a human right for natural persons regarding their possessions. In addition the measure examines if the judiciary is able to enforce property rights Heritage Foundation 2008. They usually give the creator an exclusive right over the use of hisher creation for a certain period of time.
Common property regimes typically protect the core resource and allocate the fringe through complex community norms. In the Family Code Property Relations or also referred to as Property Regimes are divided into four types. The classification of property rights regime based on the whether the resource is excludable and in nature.
 Four Types Of Intellectual Property To Protect Your Idea And How To Use Them Patent Attorney Orange County Oc Patent Lawyer
Four Types Of Intellectual Property To Protect Your Idea And How To Use Them Patent Attorney Orange County Oc Patent Lawyer
Https Www Jstor Org Stable 3989973
 Intellectual Property Rights Ipr
Intellectual Property Rights Ipr
Https Www Law Gmu Edu Assets Files Publications Working Papers 0909property10120090205 Pdf
 Property Rights Regimes And Natural Resources A Conceptual Analysis Revisited Sciencedirect
Property Rights Regimes And Natural Resources A Conceptual Analysis Revisited Sciencedirect
Https Heinonline Org Hol Cgi Bin Get Pdf Cgi Handle Hein Journals Glj84 Section 65
 What Are Property Rights Definition And Meaning Market Business News
What Are Property Rights Definition And Meaning Market Business News
Https Www Jstor Org Stable 44103323
Https Www Csus Edu Faculty S Kyle Swan Docs Lockean 20property 20rights Revised Pdf
Https Www Jstor Org Stable 2706821
 Pin By Farida On South East Asia Southeast Asia Phnom Penh Civil War
Pin By Farida On South East Asia Southeast Asia Phnom Penh Civil War
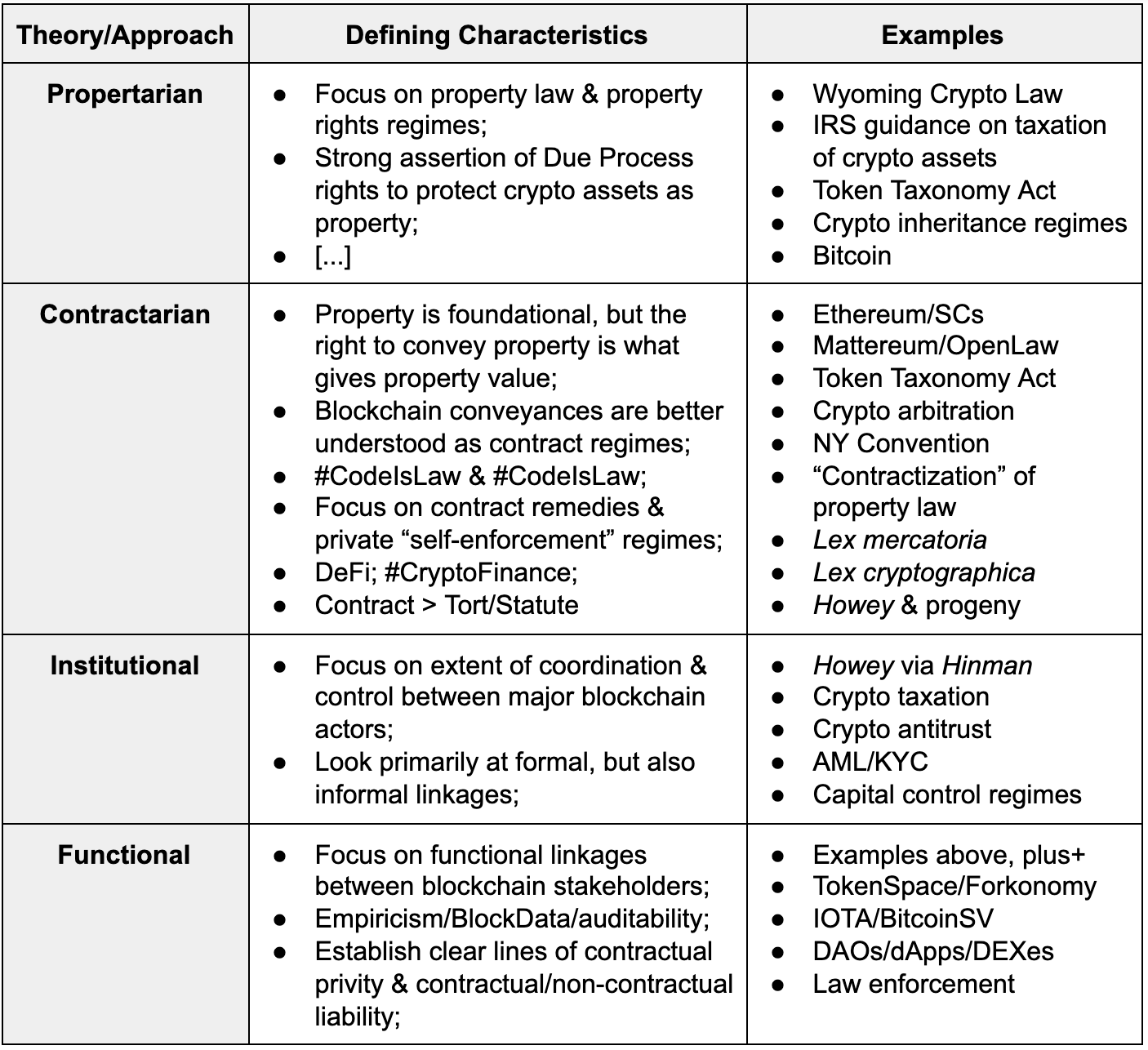 Token Taxonomy Frameworks Blockchain S Full Potential Lies Beyond By Cleanapp Crypto Law Review Medium
Token Taxonomy Frameworks Blockchain S Full Potential Lies Beyond By Cleanapp Crypto Law Review Medium
Https Www Jstor Org Stable 25798596
Why Liberals And Conservatives Flipped On Judicial Restraint Judicial Review In The Cycles Of Constitutional Time Texas Law Review
Https Www Jstor Org Stable 40215917
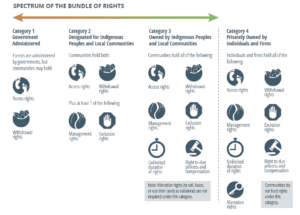 Forest And Land Tenure Rights Resources
Forest And Land Tenure Rights Resources
 Property Law Objects Subjects And Types Of Possessory Interests In Property Britannica
Property Law Objects Subjects And Types Of Possessory Interests In Property Britannica
 Combatting Antisemitism On Instagram Everyone Needs To See This Instagram Manifestation Reading
Combatting Antisemitism On Instagram Everyone Needs To See This Instagram Manifestation Reading